Online sales are not always dependent on stock availability. Retailers may offer the possibility of purchasing a product even if it is out of stock or has never been produced before. By doing so, they can optimize their revenues and reduce the overhead of maintaining higher stock levels in their warehouses. Those purchasing models are classified as backorders, preorders, and made-to-order. Throughout this article, we'll examine how each of those models works and suggest solutions to implement them properly. Furthermore, we'll introduce the dropshipping model, which relies entirely on never holding inventory.
Backorders
Merchants can offer delayed delivery options when an item is out of stock. When an order is placed, the merchant places an order with its supplier and ships it to its customers as soon as the warehouse is restocked.
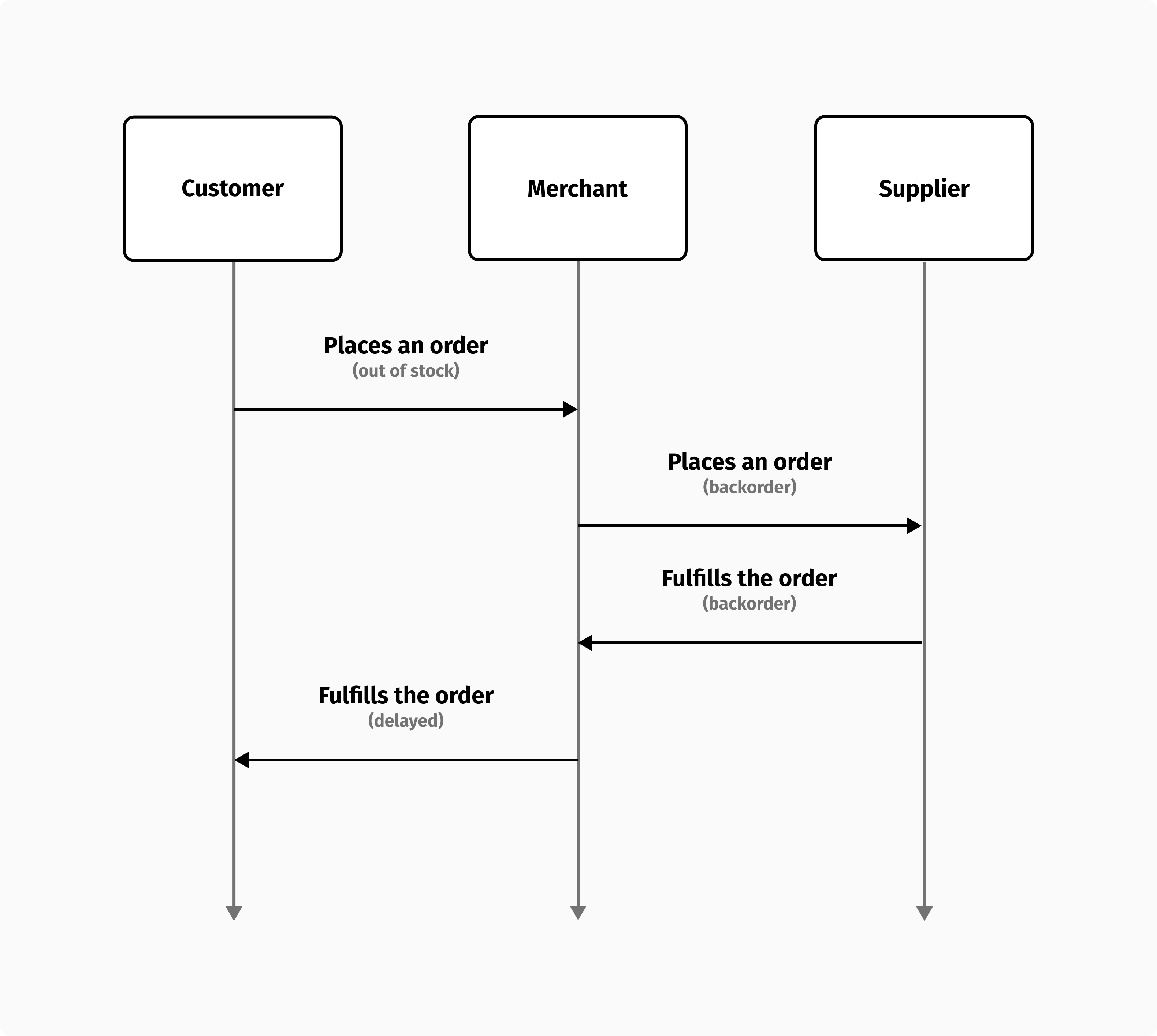
From a customer's perspective, it's just a regular order with a longer delivery time. Until the backorder is fulfilled, the merchant will hold the order. To prevent credit card authorizations from expiring, the backorder process shouldn't take too long. Otherwise, the merchant will have to request a new payment from the customer.
Preorders
In preorders, customers place orders for new products that will be available for the first time soon. Customers may wish to preorder an upcoming product to ensure their place on the waiting list. Customers who preordered the new products will get their orders shipped as soon as they are available.
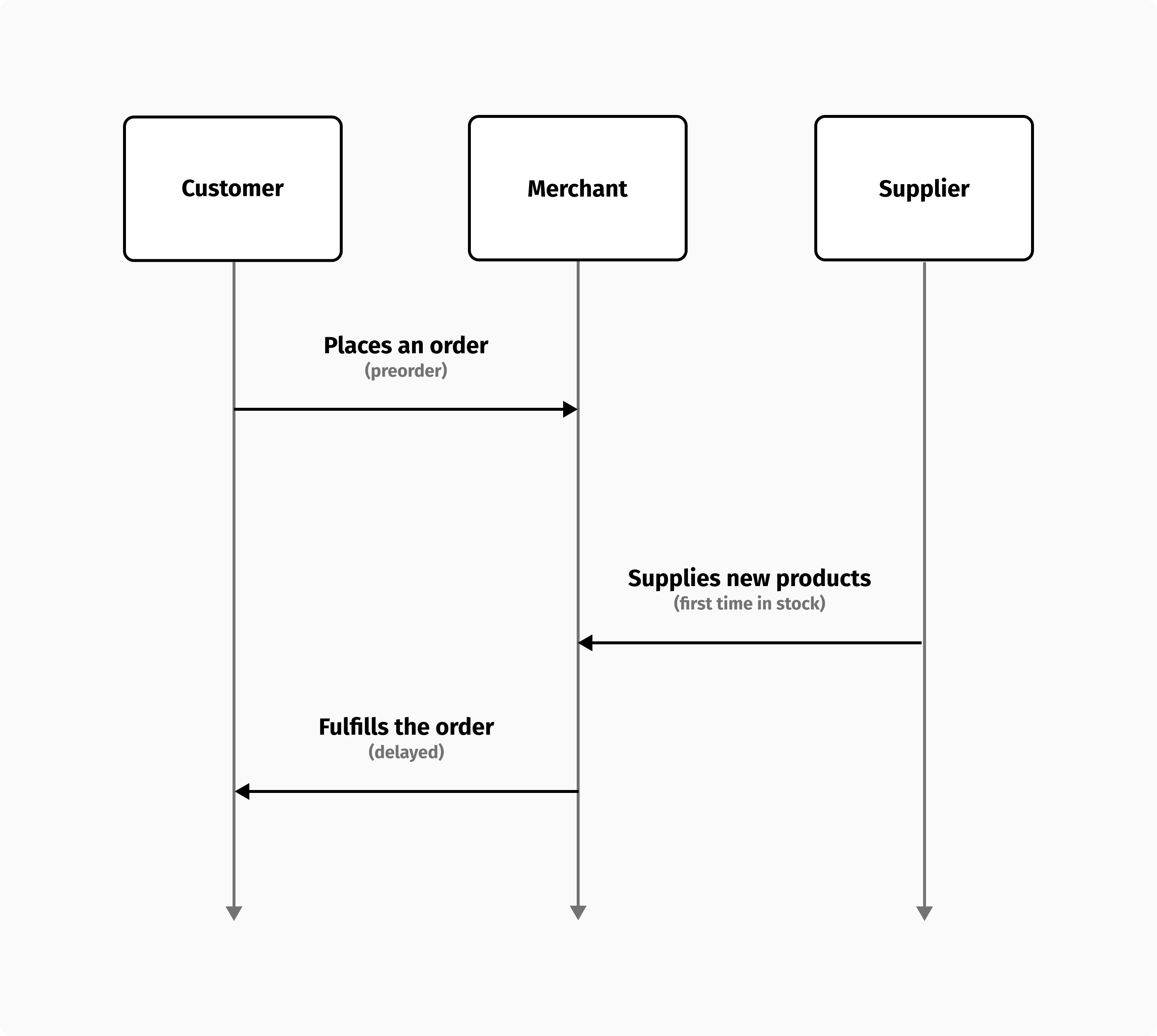
Often, credit card authorizations expire before products are available, which presents a challenge for preorders. To validate a guest customer's commitment, it may be possible to request a fraction of the payment upfront and then request the additional payment at fulfillment. You can, instead, re-authorize the payment when the order is ready to ship if the customer is registered and their credit card can be stored. It's important to remember that 3DS may trigger a new customer authorization, so the process may also involve a new customer interaction.
Made-to-order
The term "made-to-order" refers to a custom order made to the specifications of the customer. Upon receiving the order from the customer, the merchant sends it to the manufacturer, along with any special instructions. The merchant will ship the order to the customer once it's ready, but delivery will be delayed due to preparation time.
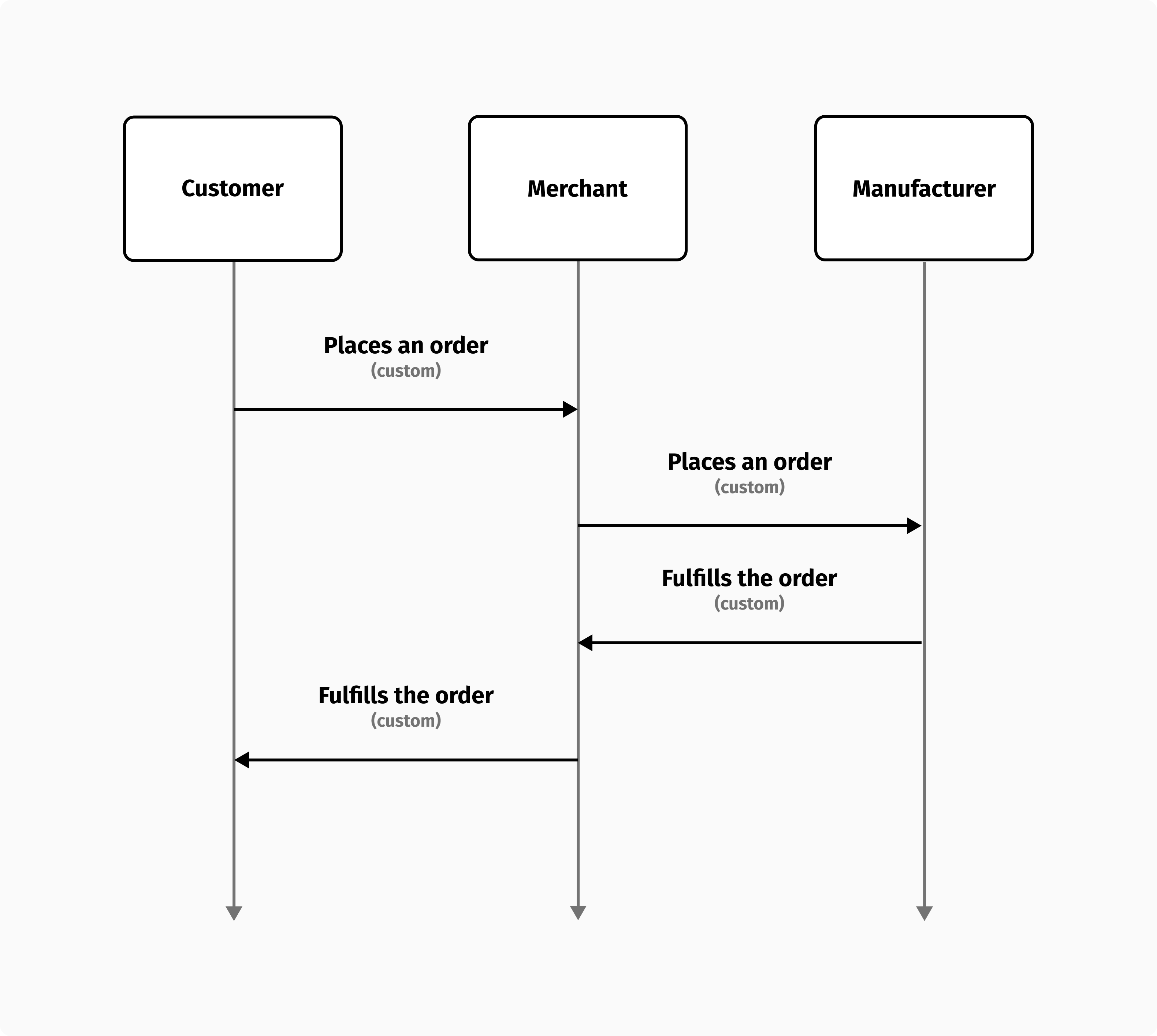
The customer should expect the delivery delay since it is a custom order. When it comes to payment, the delay between order authorization and fulfilment can be long, just like in preorders, so the same solutions can also be applied to handling payments.
Dropshipping
Using the dropshipping model, the merchant never holds inventory and places a new order with a dropshipper every time a customer purchases from their website. A dropshipper ships the order directly to the customer on behalf of the merchant, generally whitelabeling the parcel.
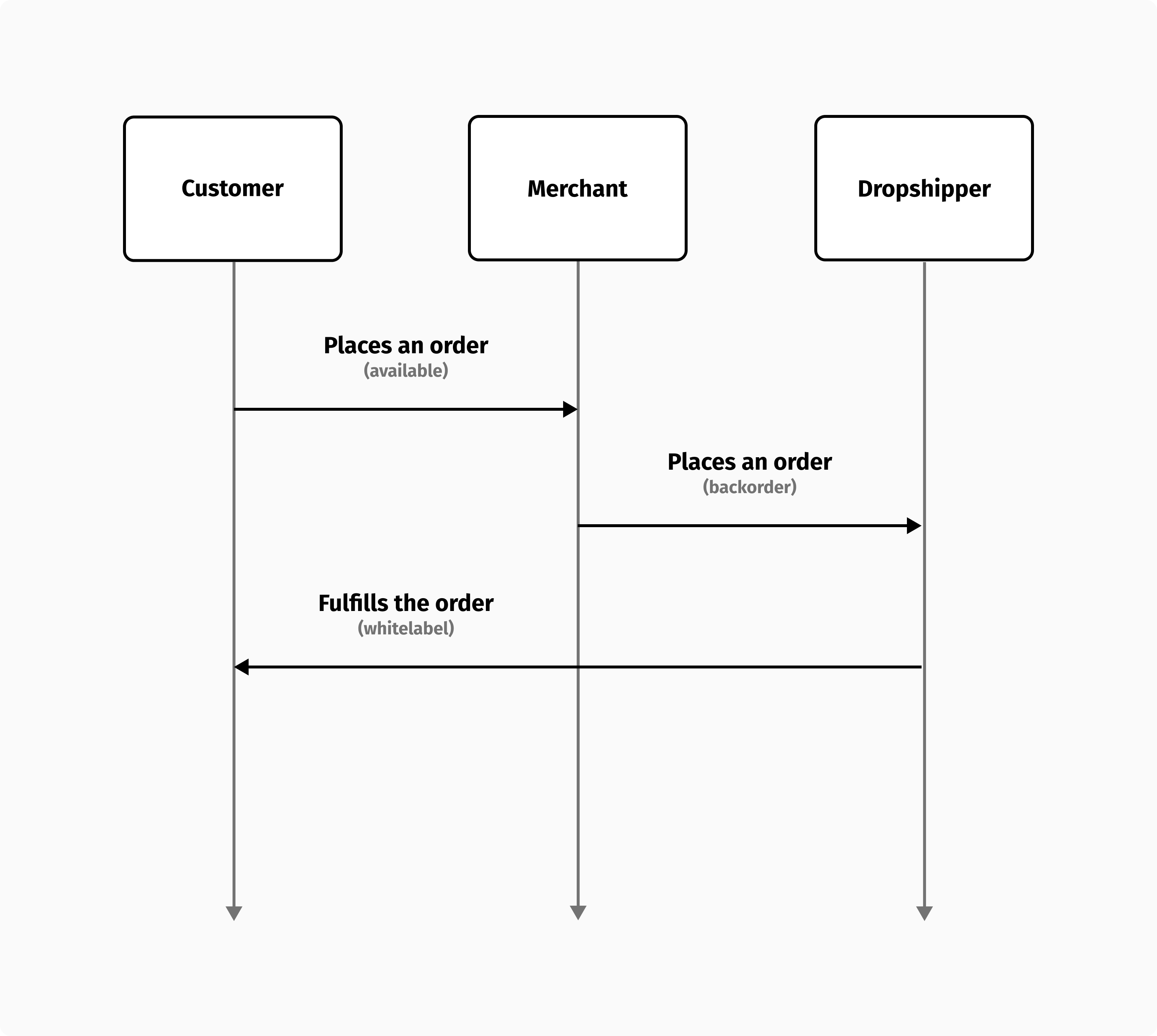
The dropshipping model reduces the risk associated with handling stock, which can make it an interesting business model. The fact that their orders will be dropshipped should be transparent to the customer. A merchant's main challenge is the lack of control over the process, so having a reliable dropshipper is essential to the success of the model. Many marketplaces use the dropshipping model, where each vendor ships their orders directly to the customer. Since the customer is generally aware of the vendor shipping the order, whitelabeling is not required.